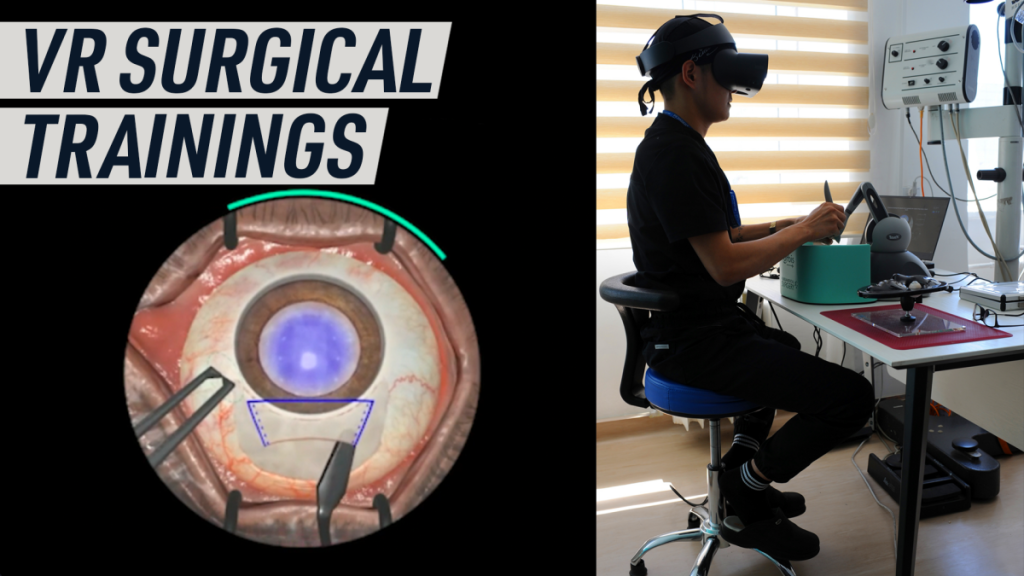
Cataracts – the cloudy patches formed on the lens of a person’s eye — are one the most common causes of blindness worldwide, according to the World Health Organisation, even though they are also among the most easily treatable eye conditions. This discrepancy is largely to due to a global shortage of ophthalmologists, which means that people, especially those in low- and middle-income countries, often live with a visual impairment that could have been prevented.
To try and increase the number of eye surgeons in those regions, an immersive training simulator designed by Orbis and FundamentalVR offers support to medical students who train in ophthalmic surgery, particularly cataract.
To create a safe, yet realistic practice environment, the simulator wields virtual reality and haptic feedback, allowing trainees to experience the feel of human tissue, and also uses cloud assessment data and accessible, low-cost gaming hardware. The programme is already running in hospitals in Ethiopia, Bangladesh, India, China, and Mongolia.